Success on the South River
As the organization shifts to a focus on keeping our entire watershed healthy, take a look back at the successful remediation efforts that have reduced the amount of mercury in the South River.
In 1929, DuPont (now Corteva) acquired acreage to build a manufacturing site for Rayon – the world’s first synthetic fiber. At the time, mercury was used as a catalyst in the production of Rayon. By the 1950s, mercury was no longer used. In 1976, DuPont discovered mercury contamination in the soil on the plant site and began working with regulatory agencies, academia, and stakeholders to study and monitor mercury in fish, water, sediment, and soil in and along the South River and South Fork Shenandoah River.
In 2001, the South River Science Team was formed to serve as a focal point for technical issues associated with mercury in the South River and downstream waterways. The team was a cooperative effort between the Virginia Department of Environmental Quality, the Department of Health; the Department of Wildlife Resources; and representatives from academia, citizen groups, the Environmental Protection Agency, and DuPont. Though DuPont no longer operates the Waynesboro plant, the company (now Corteva) continues its involvement in Waynesboro today, working to understand and remediate the mercury on and around its former site with the ultimate goal of reducing mercury levels in fish.
Through its work with the South River Science Team, Corteva learned that some of the mercury released long ago bound to soil particles in the river and then ended up being deposited on riverbanks along the South River. Today, when this riverbank soil erodes, mercury goes back into the river with it.
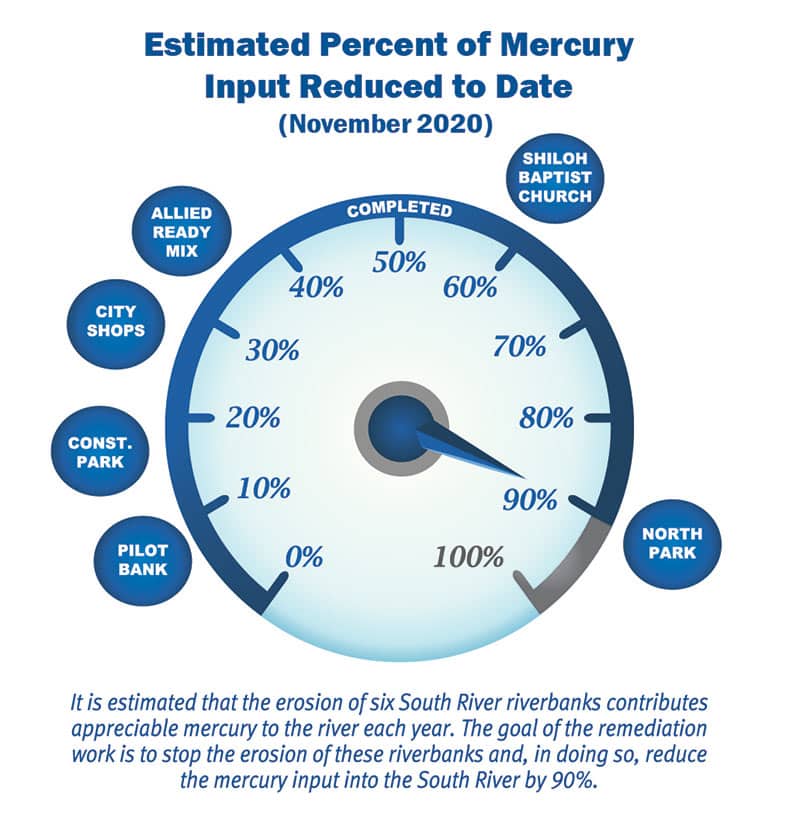
It is estimated that the erosion of six South River riverbanks contributes mercury to the river each year. The goal of the remediation work is to stop the erosion of these riverbanks and, in doing so, reduce the mercury input into the South River by 90%.
In 2009, this approach was tested on a riverbank called the Pilot Bank, and results showed that the approach successfully controlled mercury releases into the river. In 2016, DuPont began remediating and restoring additional riverbanks with elevated soil mercury levels. The first phase of work focused on specific riverbanks within two miles downstream of DuPont’s former Waynesboro plant. The remediation and restoration of all five additional locations are now complete.
Corteva collects samples before, during, and after remediation to see if remediation goals are being met. Depending on these results, additional remediation phases may be performed downstream of Waynesboro.
Nearly 5,000 feet of riverbank along the South River has been remediated to prevent erosion – that’s the length of about five cruise ships placed end to end.

Steps providing river access have been constructed and improve Greenway Trail connectivity; construction access roads have been left in place in two locations to facilitate future phases of Greenway construction.

Construction crews have logged over 38,000 hours to date on this work – the equivalent of more than four decades of non-stop work.

5,611 monitoring samples have been collected to date to evaluate the success of the remediatio
Remediation Partners









South River Remediation
Hover over areas of the map below to learn more about the remediation efforts at each site.
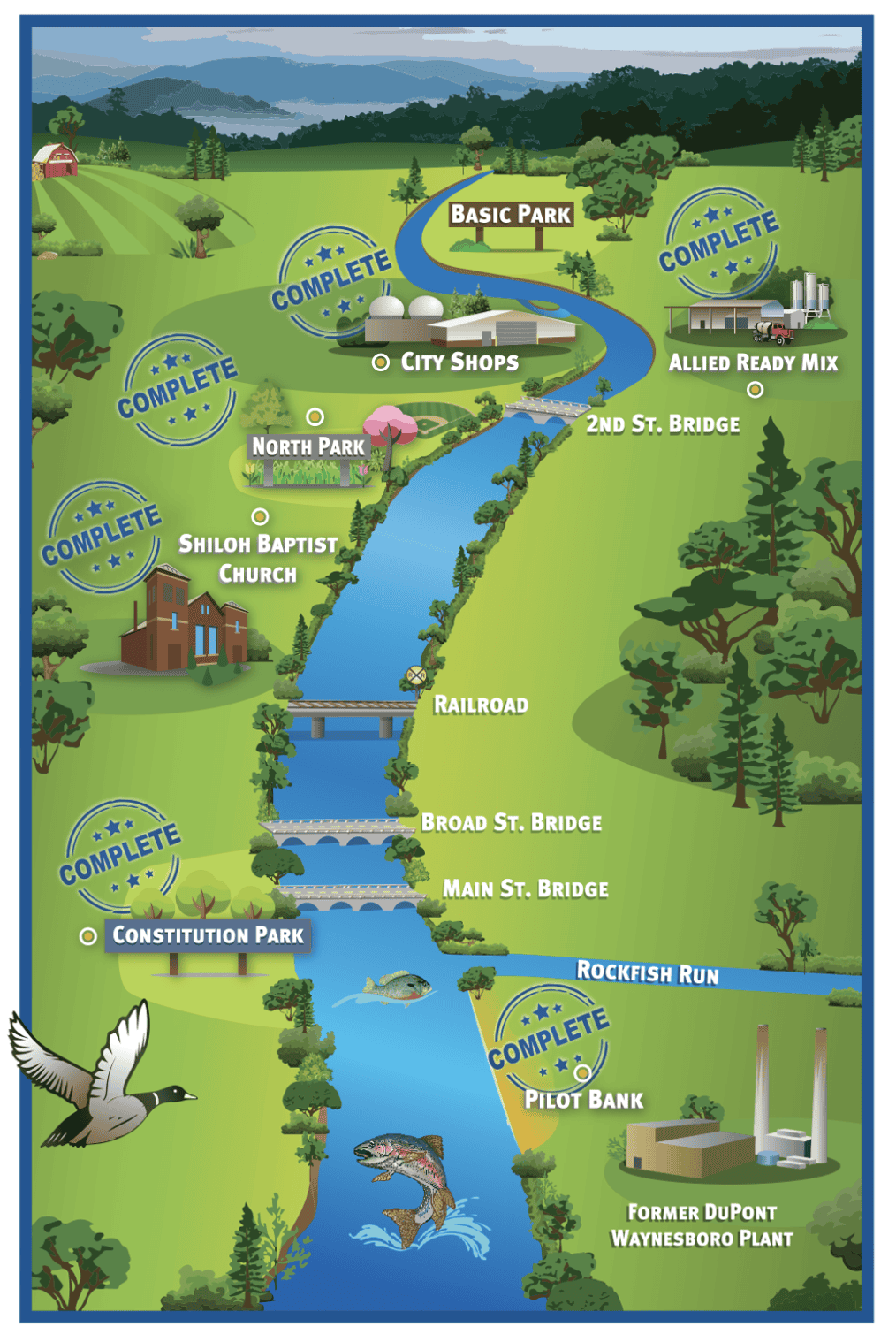
Pilot Bank
Status : COMPLETED
(click to learn more)
Constitution Park
Status : COMPLETED
(click to learn more)
Shiloh Baptist Church
Status : COMPLETED
(click to learn more)
North Park
Status : COMPLETED
(click to learn more)
City Shops
Status : COMPLETED
(click to learn more)
Allied Ready Mix
Status : COMPLETED
(click to learn more)

